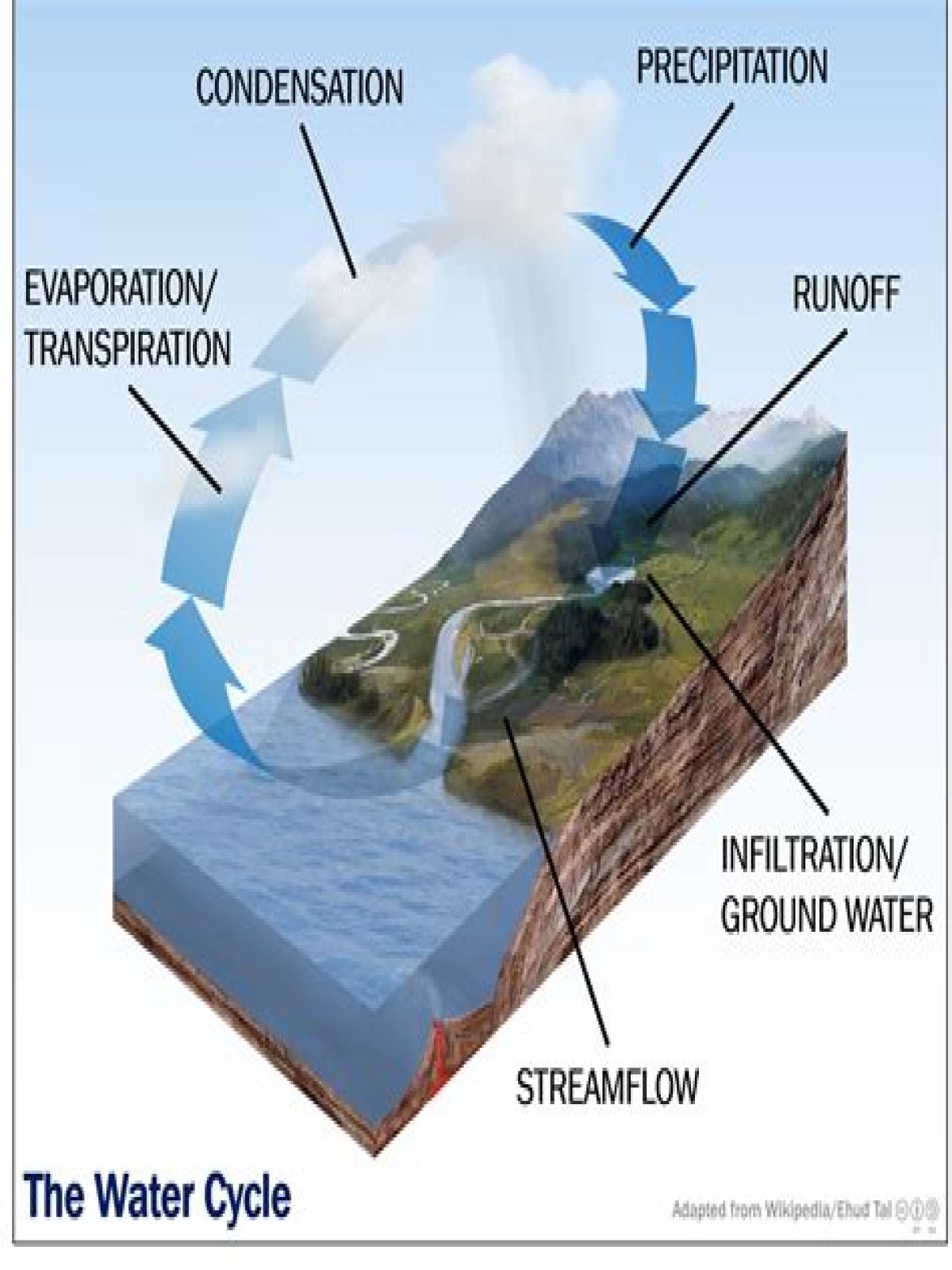
Furthermore, how is groundwater related to the water cycle?
Groundwater is a part of the natural water cycle (check out our interactive water cycle diagram). Some part of the precipitation that lands on the ground surface infiltrates into the subsurface. The part that continues downward through the soil until it reaches rock material that is saturated is groundwater recharge.
Similarly, what is the process of groundwater? Groundwater Processes. The processes involved in water entering and leaving the groundwater system are known as recharge and discharge. Recharge occurs when surface water, either from direct precipitation or from rivers and lakes, percolates downwards through the microscopic spaces in the soil and rock profile.
Secondly, what is groundwater flow in the water cycle?
In hydrogeology, groundwater flow is defined as the "part of streamflow that has infiltrated the ground, has entered the phreatic zone, and has been discharged into a stream channel, or springs and seepage water." It is governed by the groundwater flow equation.
What is the role of groundwater?
The Role of Groundwater Groundwater is an important component of the water cycle, which is the natural cycling of water through phases and locations on Earth. The water that soaks into the ground sometimes comes back out above ground in other locations, feeding the world's rivers, lakes, streams, and oceans.
What are 3 ways water is stored?
How the water cycle works step by step?
What is mean by ground water?
How much water is there in the world?
What affects groundwater flow?
What is the main source of groundwater?
What is discharge water cycle?
How groundwater is stored?
What is the rate of groundwater flow?
How do you measure groundwater flow?
What are the different types of groundwater?
- Rivers.
- Lakes.
- Natural springs.
- Rain.
- Snow.
- Glaciers.
- Aquifers etc.